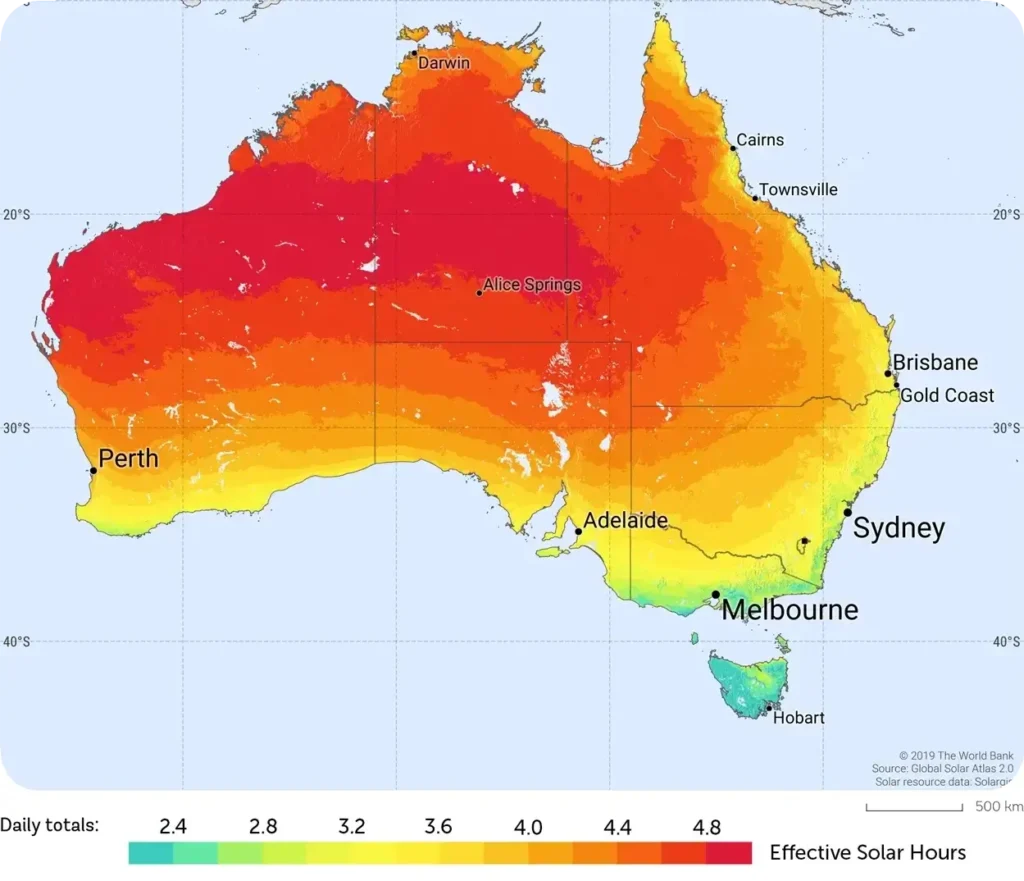
In recent years, solar energy has emerged as a cornerstone of Australia’s renewable energy transition, playing a pivotal role in reducing carbon emissions and promoting environmental sustainability. This blog explores the profound impact of solar energy on Australia’s quest to achieve its carbon reduction goals, focusing on its environmental benefits and significance in combating climate change.
1. Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
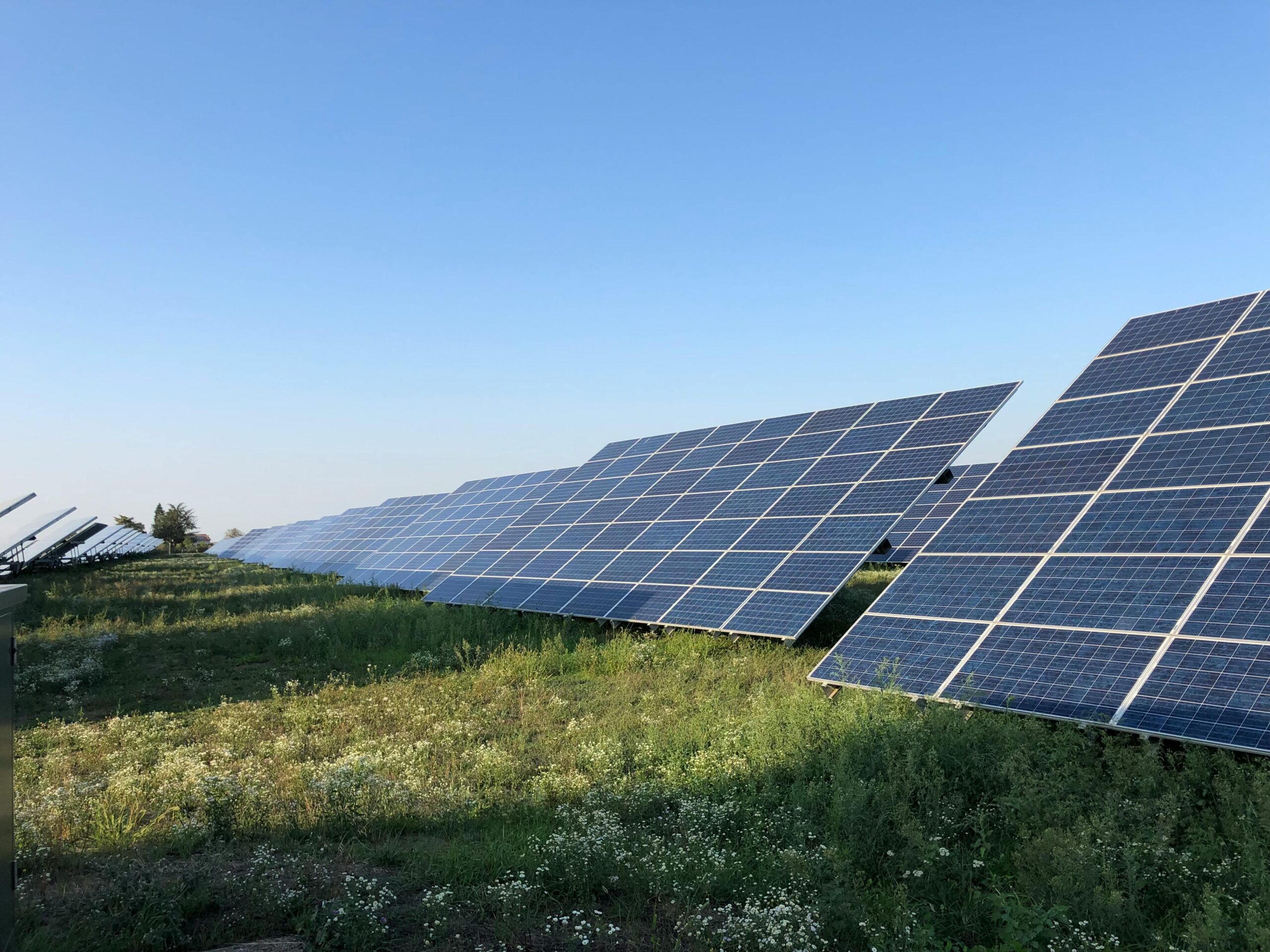
Solar energy offers a myriad of environmental benefits, making it a key player in Australia’s sustainable future. Firstly, solar power produces electricity with zero greenhouse gas emissions, significantly reducing carbon dioxide and other pollutants that contribute to climate change. By harnessing the abundant sunlight available across the continent, solar energy helps minimise Australia’s reliance on fossil fuels, thus curbing air and water pollution associated with traditional energy sources.
2. Role in Achieving Carbon Reduction Goals
Australia has committed to reducing its carbon emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change, and solar energy is instrumental in achieving this ambitious target. With its clean and renewable nature, solar power contributes significantly to the country’s renewable energy mix, displacing carbon-intensive sources such as coal and natural gas. The widespread adoption of solar panels in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors further accelerates the transition towards a low-carbon economy, paving the way for a sustainable future.
3. Solar Energy Policies and Initiatives
Australia’s commitment to harnessing solar energy is reflected in its policies and initiatives aimed at incentivising renewable energy adoption. The Renewable Energy Target (RET) scheme, along with various state-based feed-in tariff programs, provides financial incentives for installing solar panels and encourages investment in solar infrastructure. Additionally, government-funded research and development projects focus on advancing solar technology and improving efficiency, driving innovation in the renewable energy sector.
4. Economic and Social Implications
Beyond its environmental benefits, solar energy contributes to Australia’s economic growth and social well-being. The solar industry creates jobs, stimulates investment, and fosters innovation, particularly in regional areas where solar farms and manufacturing facilities are located. Moreover, solar power enhances energy security by diversifying the energy mix and reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels, thus promoting resilience and self-sufficiency in energy supply.
5. Future Outlook and Opportunities
Looking ahead, the future of solar energy in Australia appears promising, with ample opportunities for further expansion and integration. Advances in technology, such as energy storage solutions and grid modernisation, will enhance the reliability and flexibility of solar power, enabling greater penetration into the energy market. Moreover, continued government support and public awareness campaigns will drive continued growth in solar adoption, solidifying its position as a cornerstone of Australia’s renewable energy transition.
As Australia grapples with the challenges of climate change and strives to achieve its carbon reduction goals, solar energy emerges as a beacon of hope and progress. By harnessing the abundant sunlight that bathes the continent, solar power offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution to meet the country’s growing energy needs. With ongoing advancements in technology and supportive policies, solar energy is poised to play an increasingly significant role in shaping Australia’s energy landscape and driving environmental sustainability for generations to come.
Get in touch to receive a quote today!