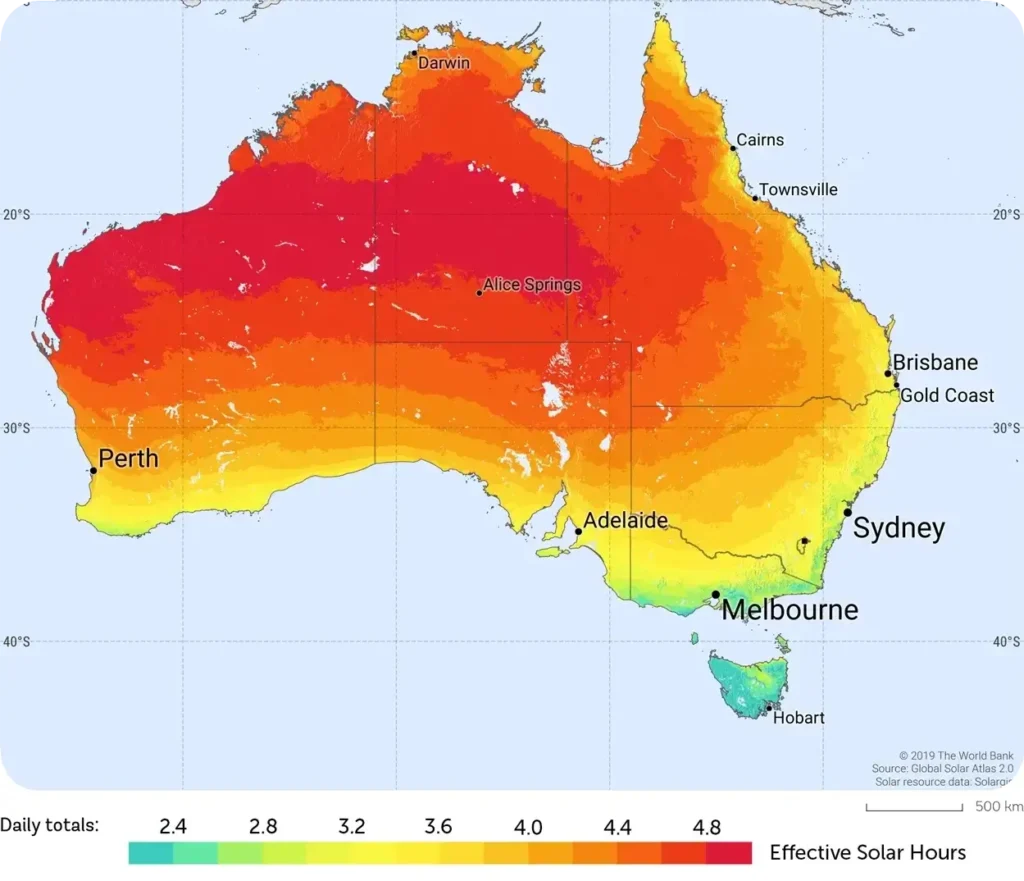
Imagine a life unshackled from the grid, empowered entirely by the sun, where self-sufficiency is not just a concept but a daily reality. Rising each morning, not to the hum of electrical lines, but to the whispers of nature and the quiet assurance of a solar-powered home, is a dream for many.
For those seeking freedom from traditional energy sources, mastering an offgrid solar system offers not only a blueprint for independence but also a robust survival guide for the future.
With the growing interest in sustainable living and the increasing unpredictability of central power supplies, understanding how to harness the sun’s power for your off-grid needs has never been more crucial.
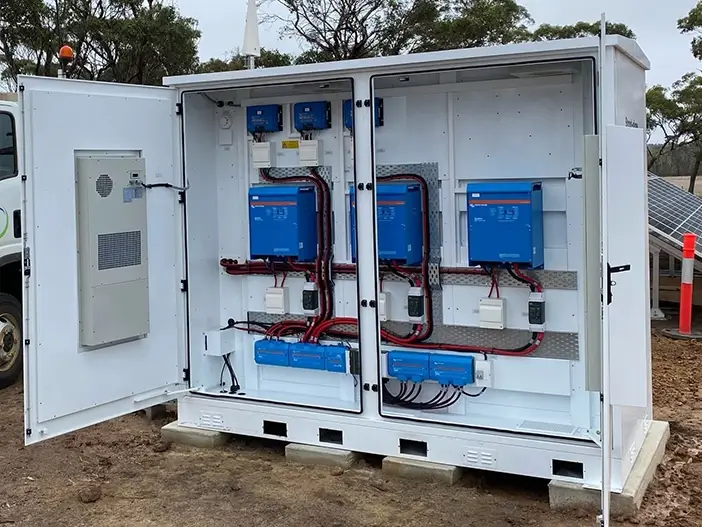


Understanding OffGrid Solar Systems: Key Concepts and Beliefs
Before diving into the specifics of off grid solar systems, it’s important to grasp the key concepts and benefits of this alternative energy solution.
An off grid solar system is a self-contained power generation and storage system that operates independently from the traditional electrical grid.
It captures the sun’s energy using solar panels, converts it into usable electricity through inverters, and stores excess power in batteries for times when sunlight is insufficient or non-existent.
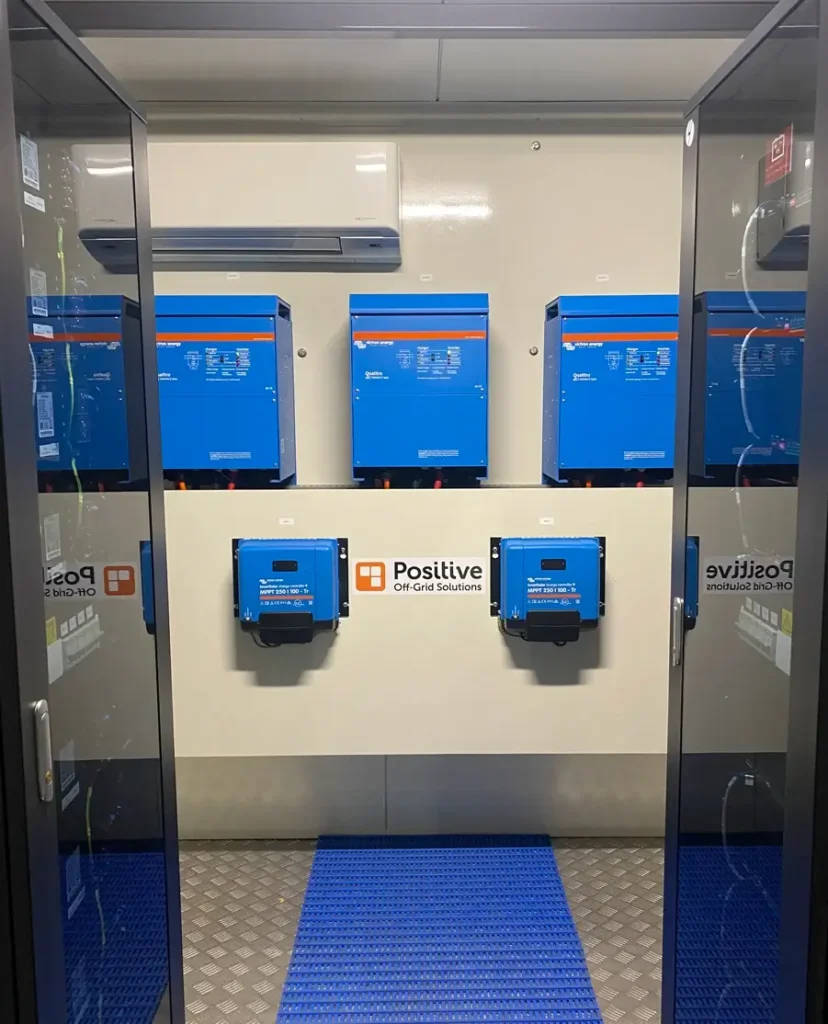
The Core Components of an Off-grid Solar System
At its heart, an off-grid solar system is composed of several indispensable components:
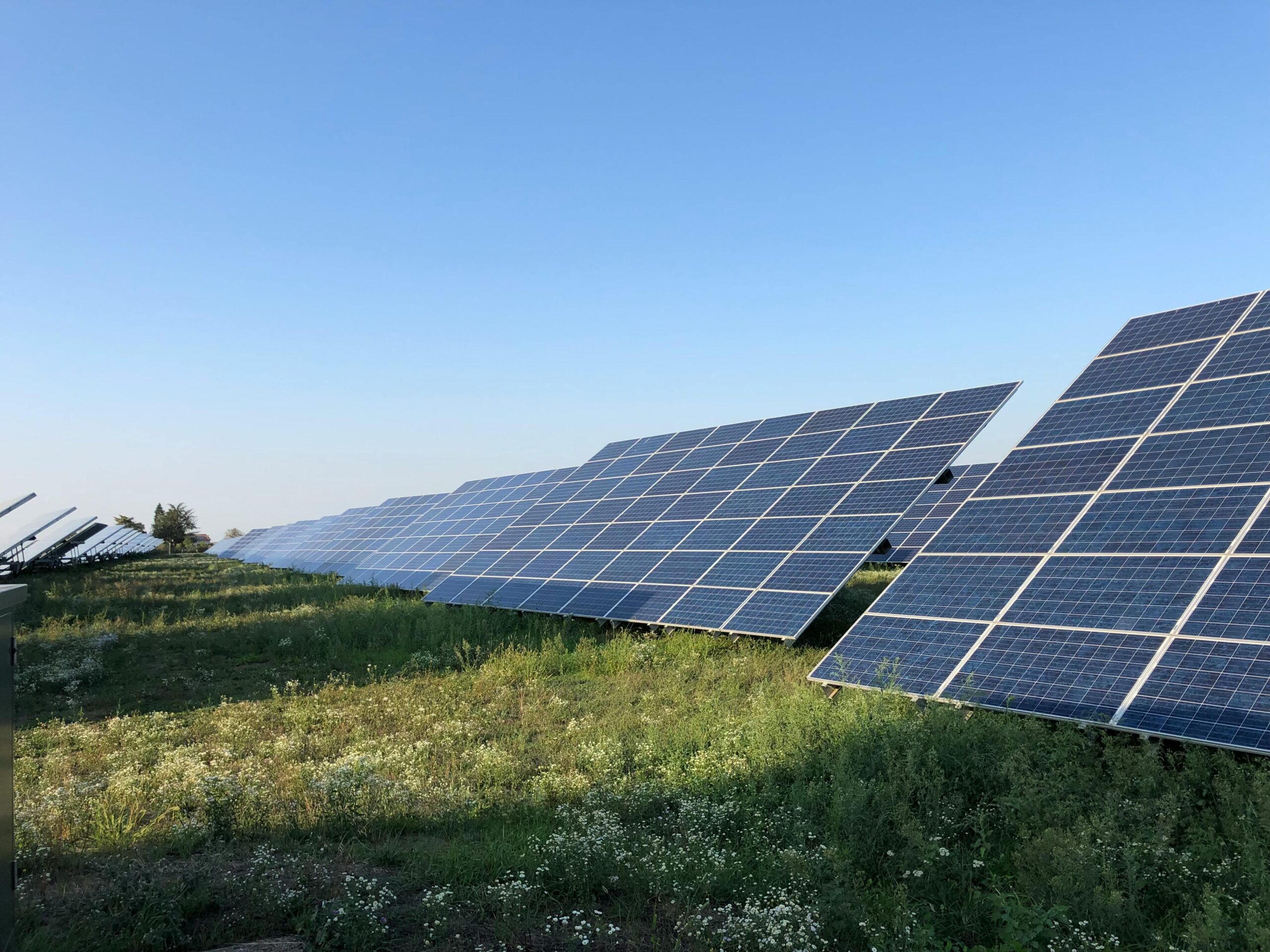
– Solar Panels: These are responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into electrical energy. The various types of solar panels include monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels, each offering unique advantages and efficiency levels.
– Inverters: These devices convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into the alternating current (AC) electricity required for household appliances. String inverters, microinverters, and hybrid inverters are some of the common types.
– Batteries: These store excess energy produced during peak sunlight hours for use when sunlight is limited. Deep-cycle batteries, such as lead-acid and lithium-ion, are typical in off-grid applications due to their durability.
– Charge Controllers and Other Accessories: These manage the flow of electricity, ensuring that batteries are charged correctly and that no damage occurs from overcharging or deep discharging.
Understanding these components and how they interact is crucial for designing a reliable and effective off-grid system. This knowledge informs decisions on system sizing, component selection, and long-term maintenance strategies.
Benefits of Off-Grid Power Systems
- Provide electricity in remote areas: One of the primary benefits of an off grid solar system is its ability to provide electricity in remote areas where grid access is limited or non-existent. This makes it an ideal solution for cabins, rural homes, or even mobile homes.
- Environmental Impact: Another significant advantage is the environmental impact. By relying on clean energy from the sun, off grid systems reduce carbon emissions and contribute to the fight against climate change. Furthermore, off-grid solar systems provide resilience during power outages.
- Energy Independence: Traditional grid-connected homes are vulnerable to blackouts or natural disasters that disrupt the power supply. Off grid systems, on the other hand, continue to provide electricity independently, which can be crucial in emergency situations or areas prone to frequent power interruptions.
- Long Term Savings
Although the initial setup cost can be significant, solar systems can reduce or eliminate electricity bills in the long run.
The Essential Components of an Off-grid Solar System
Understanding the essential components of an off grid solar system is key to designing a system that meets your energy needs efficiently and reliably.
Let’s explore each component in detail to understand its role and how it can optimise the performance of your off-grid setup.
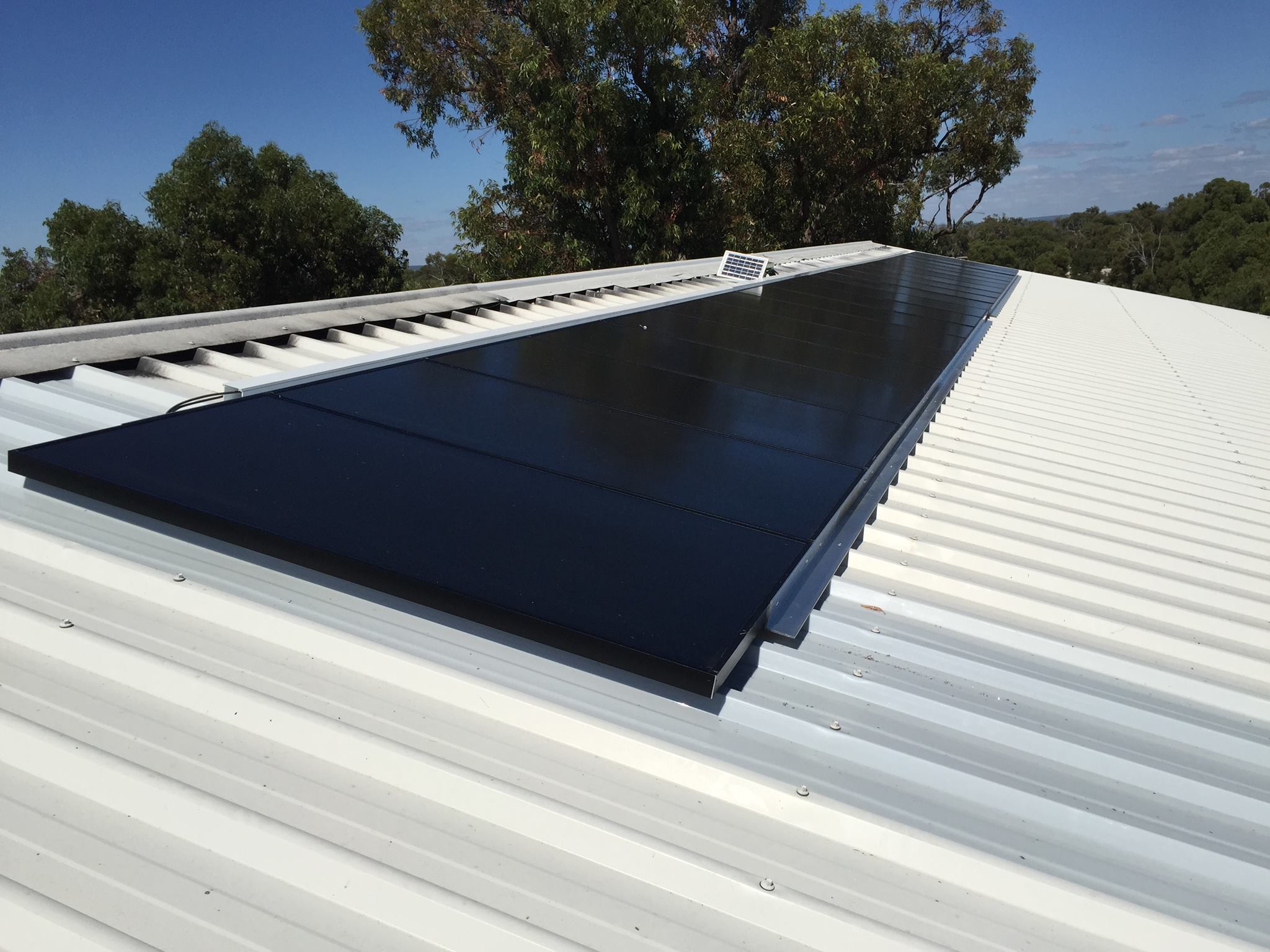
Solar Panels: Types, Efficiency, and Installation
Solar panels are the keystone of any off-grid solar system.
They capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy through the photovoltaic (PV) effect, where photons from sunlight knock electrons free from atoms, generating a flow of electricity.
Types of Solar Panels
– Monocrystalline Solar Panels: These are made from a single continuous crystal structure, usually silicon. Known for their high efficiency and longevity, monocrystalline panels perform well even in low-light conditions. Their sleek black appearance also makes them aesthetically pleasing.
– Polycrystalline Solar Panels: These are composed of multiple silicon crystals. They are generally more cost-effective but offer slightly lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline panels. Their characteristic blue color comes from the various crystals used.
– Thin-Film Solar Panels: These are created by depositing one or more layers of photovoltaic material on a substrate. Thin-film panels are lightweight, flexible, and less affected by shading but typically have lower efficiencies compared to crystalline silicon panels.
Efficiency and Installation Tips
The efficiency of solar panels, whether for a solar system for home or solar system for commercial use, refers to their ability to convert sunlight into electricity.
While monocrystalline panels generally have higher efficiency rates, the difference between these and other types may not always be significant enough to outweigh considerations of cost or space.
For optimal performance, it is crucial to install panels at the correct orientation and tilt.
Typically, panels should face south in the northern hemisphere and north in the southern hemisphere to maximise sunlight exposure.
The tilt angle should correspond to your location’s latitude. The closer to the equator, the lower the tilt angle, versus the further away from the equator, the greater the required tilt angle.
Regular cleaning and maintenance are also essential to ensure that panels operate at peak efficiency. Dust, dirt, and debris can reduce their performance, so periodic cleaning is recommended.
Inverters: Types, Sizing, and Importance
Inverters are vital in off grid systems as they transform the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity that powers household appliances.
Different types of inverters serve various needs:
–String Inverters: Most common in residential systems, these connect several solar panels in series (a string). They are cost-effective but can suffer from reduced efficiency if any panel in the series is shaded or malfunctions.
– Microinverters: These are installed on each individual solar panel, allowing for independent operation and optimization. This setup mitigates the impact of shading or malfunctions on overall system performance.
– Hybrid Inverters: These combine functionalities such as battery charging and grid-connection capabilities, providing additional flexibility for off grid systems.
When choosing an inverter, it is crucial to size it appropriately based on your total power consumption.
An undersized inverter may fail to meet peak loads, while an oversized one could lead to inefficiency and unnecessary costs.
Some inverters come with built-in features like battery chargers, adding versatility to your system.
Batteries for Off-grid Living: Types, Maintenance, and Lifespan
Batteries store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight.
Deep-cycle batteries are preferred for offgrid applications due to their ability to endure frequent charge and discharge cycles.
Types of Batteries
– Lead-Acid Batteries: These are traditional, cost-effective options available in flooded (requiring maintenance) and sealed (maintenance-free) varieties.
Flooded lead-acid batteries need regular electrolyte checks and water topping, while sealed batteries are more convenient but generally have a shorter lifespan.
– Lithium-Ion Batteries: Offering higher energy density, longer lifespan, and faster charging times, lithium-ion batteries are lightweight and compact. Although they are more expensive, their long-term benefits often justify the upfront cost.
Maintenance and Lifespan Improvement
Proper battery maintenance is critical for prolonging life and ensuring reliable performance. Regular monitoring of battery voltage levels, periodic equalising charges, and avoiding extreme states of charge (overcharging or deep discharging) are essential practices. Correct sizing based on capacity and voltage requirements also plays a crucial role in maximising battery lifespan.residential
Sizing Your Off-grid Solar System: Calculating Energy Needs
Accurately sizing your off grid solar system is paramount to ensure it meets your energy requirements without the risks of over or under-sizing. The process involves calculating your daily energy consumption and accounting for location, climate, and available sunlight.
Steps to Size Your System
1. List Appliances and Devices: Identify all the appliances and devices you plan to power with your off-grid system, noting their power consumption in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
2. Estimate Usage: Estimate the number of hours each appliance or device will be used daily.
3. Calculate Daily Consumption: Multiply the power consumption (W) by daily usage hours for each item to get their daily energy consumption in watt-hours (Wh).
4. Sum Total Daily Consumption: Add the daily energy consumption of all appliances and devices to determine your total daily energy requirement.
Accounting for Inefficiencies and Environmental Factors
It is crucial to add a buffer to your calculations to account for inefficiencies in the system and periods of limited sunlight. Multiply your total daily energy consumption by a factor that considers these losses to estimate the required capacity for your solar panels and batteries.
Tools such as online calculators and consulting with professionals can help ensure accurate sizing tailored to your local conditions and specific energy needs.
To simplify the process, we have built a calculator into this website to streamline your estimations with Load Assessment Questionnaire.
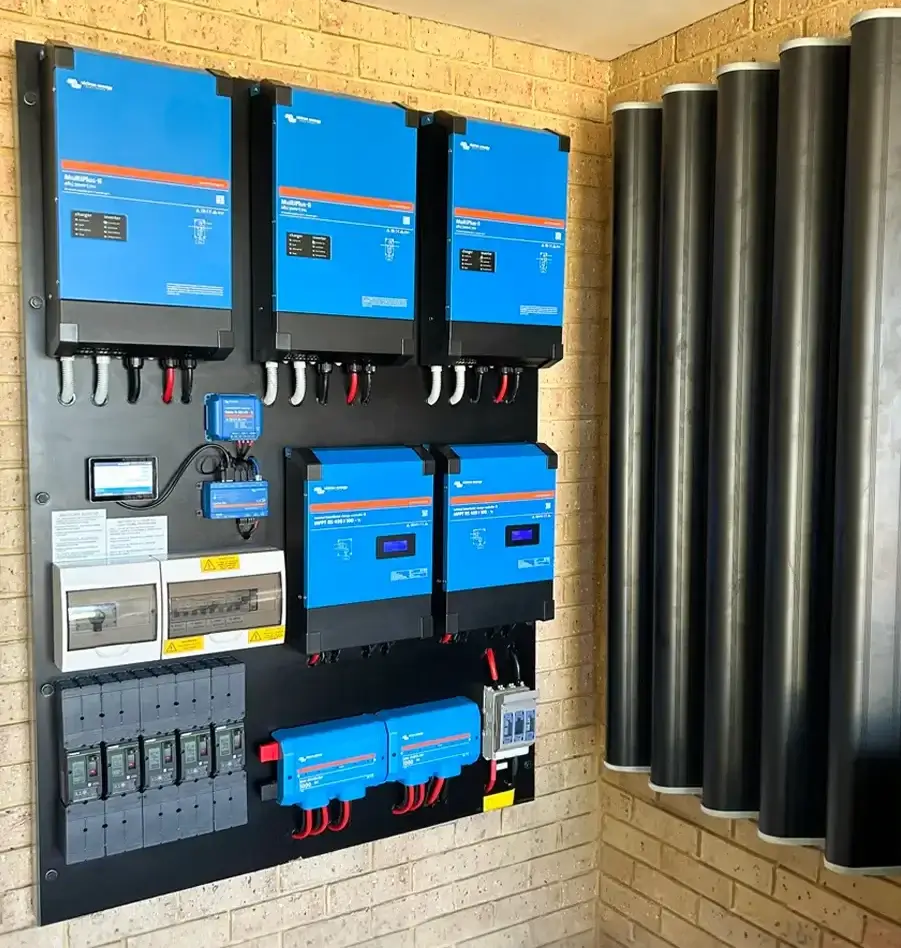

Designing for Energy Efficiency in Off-grid Homes
The overall design of your off-grid home significantly impacts energy efficiency. By focusing on strategic design elements and choosing the right appliances, you can minimize energy consumption without compromising comfort or functionality.
Key Design Considerations
– Insulation: Effectively insulating walls, floors, and roofs reduces the need for heating and cooling, maintaining indoor temperature efficiently.
– Passive Solar Design: Orienting your home and using design features that maximize natural light and heat gain during winter while minimizing them in summer reduces reliance on artificial lighting and climate control.
– Natural Ventilation: Incorporating windows, skylights, and vents that enhance cross-ventilation helps cool your home naturally, reducing the need for air conditioning.
– Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors: Install windows and doors with low-emissivity (low-e) coatings and insulated frames to minimize energy loss and maximize natural light.
Renewable Energy Integration
Besides solar power, consider integrating other renewable energy sources like wind turbines or micro-hydro generators to diversify your energy supply and improve resilience.

Financial Considerations: Cost Analysis and Long-Term Savings
Financial planning is a critical aspect of developing an off-grid solar system. Understanding the cost implications and potential long-term savings is vital for making informed decisions.
Evaluating Initial Investment and Long-Term Savings
Off-grid systems typically involve higher upfront costs compared to grid-connected solutions. However, the long-term savings from reduced electricity bills and independence from rising energy prices often justify this initial investment.
–Cost of Grid Electricity: Compare the current and projected costs of grid electricity with the investment required for an off-grid system.
– Government Incentives and Rebates: Research available government incentives or rebates for renewable energy installations, which can significantly reduce the upfront costs.
Total Cost of Ownership
Calculate the total cost of ownership over the system’s lifespan, including initial setup, maintenance, and replacements. Compare this with the expected savings on energy bills to determine the payback period and overall financial viability.
Investing in Quality Equipment
Choosing high-quality equipment, though potentially more costly initially, ensures better performance, durability, and longer lifespan. This can lead to reduced maintenance and replacement costs, ultimately saving money.
Off-grid Solar System vs. Diesel Generators: A Cost-Effective Comparison
When considering off-grid power solutions, it’s important to compare off-grid solar systems with traditional diesel generators (gensets) to evaluate long-term cost-effectiveness.
Key Factors in Comparison
– Fuel Costs: Diesel generators require a constant supply of fuel, which is subject to price fluctuations and availability. Solar systems, by contrast, harness free and abundant sunlight.
– Maintenance Costs: Generators need regular servicing, including oil changes and filter replacements, adding to ongoing costs. Solar systems require minimal maintenance after installation.
– Environmental Impact: Diesel generators emit pollutants and noise, whereas solar systems are silent and have zero emissions during operation.
Financial Planning for Successful Off-grid Living
Effective financial planning involves budgeting, cost analysis, and setting realistic savings goals. This process is essential for ensuring the sustainability and success of your offgrid lifestyle.
Importance of Budgeting and Cost Analysis
Create a detailed budget to track income and expenses, ensuring that essential needs such as food, water, shelter, and healthcare are covered. Analyse costs associated with the off-grid lifestyle, including the initial investment in solar systems and daily living expenses.
Long-Term Savings and Emergency Preparedness
By investing in an efficient off-grid system and adopting energy-saving habits, you can reduce reliance on external power sources and achieve significant long-term savings. Financial planning also includes setting aside funds for emergencies or unexpected repairs, ensuring financial stability.

Embracing Resilience: Thriving in an Off-grid Environment
Living off-grid encourages resilience through self-sufficiency, community support, and adaptability. It empowers individuals to generate their own power, grow their own food, and manage resources efficiently.
Advantages of Sustainable Energy Solutions
Off-grid solar systems reduce dependence on fossil fuels and offer a reliable energy source immune to grid failures. This sustainable approach aligns with broader environmental goals and personal values of independence and resilience.
Building Community and Adaptability
Building strong, supportive communities enhances resilience. Sharing knowledge and resources can help individuals and groups adapt to challenges and uncertainties that may arise.

Conclusion: Embracing Resilience Through Off-grid Solar Mastery
Mastering off-grid solar systems provides a path to a resilient and self-sufficient future. By understanding the essential components, accurately sizing your system, prioritizing energy efficiency, making informed financial decisions, and embracing a resilient lifestyle, you can achieve true independence from the grid. Off-grid solar systems empower you to live sustainably, reduce carbon footprints, and maintain control over your energy needs, ensuring a robust and adaptable lifestyle in an unpredictable world.
Embrace the opportunity to create your own resilient energy infrastructure, paving the way for a sustainable and autonomous future where you are not only surviving but thriving. Taking the initiative to master off-grid solar systems today will enable you to unlock the secrets to a truly independent and sustainable lifestyle, rich with the benefits of self-sufficiency, resilience, and harmony with nature.